Feeding your brain is essential for every function we perform. Your brain is sometimes referred to as the “control center” of your body. Beyond helping you to think and remember clearly, your brain helps to regulate the rest of your body, like your breathing, temperature, hunger, and hormones. It’s important to keep your brain as healthy as possible for as long as possible to stave off chronic—often incurable—diseases like Alzheimer’s, and science shows us how to do this.
Your brain’s health is influenced by six fundamental pillars:
- Exercise
- Stress reduction
- Sleep and relaxation
- Socialization
- Medications and supplements
- Food and nutrition
In this article, we’ll go through each one of these pillars of brain health before diving deeper into specific and actionable strategies surrounding food and nutrition.
Exercise for brain health
Exercise is incredibly beneficial for physical and mental fitness, to de-stress, improve sleep, as well as keep your heart, lungs, and muscles healthy. What’s more, being physically active is a fundamental pillar of brain health. There are several types of exercise and all are beneficial.
Aerobic exercise, also known as “cardio” or “endurance” exercise, helps to get your heart rate up and your muscles warm. Examples of aerobic exercises include biking, swimming, running, and climbing stairs. This type of exercise benefits your brain because it helps to preserve existing brain cells and also promotes the growth of new ones.
Another type of exercise is strength or “resistance” training such as pushing or pulling weights or other heavy objects (like groceries). This is known to help build and maintain strong bones. Strength training also helps your brain by enhancing your concentration and improving your decision-making skills.
Stress reduction for brain health
We all experience stress. Stress is how the body and brain react to a threat or stressor. These reactions are often called “fight or flight.” They include increased heart rate and breathing and a heightened sense of focus. All of these physiological reactions are initiated by the brain when it detects the threat.
Once the threat is gone, the stress response relaxes and your body and brain can regain their normal balance. However, sometimes that stress lingers on for days, weeks, and months and becomes longterm stress. It’s this chronic stress that can negatively impact your brain. Chronic stress can effectively shrink the part of your brain responsible for memory and learning in your prefrontal cortex and can increase the part of your brain, the amygdala, that is receptive to stress.
While stress cannot be eliminated entirely you can learn effective techniques to better manage it and preserve your brain health. One very practical—but often difficult—strategy is to “just say no” to things you don’t actually have to do. Turning down unnecessary opportunities to take on more responsibility may help reduce the amount of stress you feel.
Another strategy to reduce stress is to focus on the specific problem at hand in the present moment. This can help you see the current situation more clearly and make better decisions, to avoid turning it into an unmanageably large issue or perceiving the situation to be more difficult than it has to be.

Finally, calming the mind through meditation or guided imagery can help reduce the feelings of stress by refocusing your attention on something positive and soothing.
Sleep for brain health
Getting your 7-9 hours of sleep each night helps your mood and ability to manage stress. Sleep also allows you to be better able to plan and run your busy life and ensure that you can have the energy to do what you need to do to maintain and improve your well-being .
One of the most important things you can do to get enough sleep is to foster a regular sleep schedule. By going to bed and waking up at about the same time every day—including weekends and when you’re traveling—you “train” your body and brain to get on a healthy sleep schedule.
Another strategy to help you get more sleep is to create a relaxing bedtime routine. That routine can start an hour or more before you need to sleep and can include things like dimming lights, putting your screens ( such as TV, internet, or smart phone) away, listening to soothing music or reading a book, or having a warm relaxing bath.
Whatever helps you get your sleep is going to also help your brain.
Socialization
Staying connected to a network of people you care about can help reduce stress, improve mood, and help to feel more supported in life. Your social network can include your spouse and/or partner, immediate and extended family members, friends, or others in your community.
You can socialize informally or spontaneously (like walking or chatting with a neighbor) or you can join organized activities like hobby groups, sports teams, or volunteering opportunities. The brain benefits of socializing even extend beyond people to pets. Studies show that pets can help you feel calm, improve your health, and enhance your social life, all of which can benefit your brain.
Medications and supplements
Depending on your personal health situation, you may be advised to take medications or supplements. These can be important to reducing your risks for serious conditions and slowing down the progression of diseases. Some of the medical conditions that are linked to deteriorating brain health include high blood pressure, diabetes, and excess weight. These can increase your risks of cognitive decline (reduced memory and ability to think) and developing dementia.
If your doctor is recommending medications or your registered dietitian is recommending supplements, be sure to take them as directed and go for routine monitoring or testing as required.
Food and nutrition to feed your brain
There are several foods and nutrients that promote a healthy brain by slowing cognitive decline and reducing your risk of Alzheimer’s disease. University researchers developed the MIND diet to emphasize foods that are rich in antioxidants and critical brain nutrients such as vitamins and other plant-based phytochemicals.
Here are some key foods and nutrients to boost your brain health.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are a group of essential fats that promote heart and brain health. Some of the best sources of omega-3s are fatty fish such as salmon, herring, and sardines. The MIND diet recommends at least one serving of fish each week. If you don’t love fish, omega-3s are also found in nuts and seeds such as flax, chia, walnuts, and soy.

More plants
Plants contain more than vitamins and minerals, they’re also a source of fiber and phytochemicals. Eating more plants helps more than only your brain, it’s also associated with better heart health and weight maintenance. If you want more ideas and inspiration for plant-focused eating, I invite you to subscribe to my free weekly healthy recipe here.
Some of the top plants for brain health are deeply-colored fruits and vegetables like berries, leafy greens, and broccoli. The MIND diet recommends vegetables every day, at least six servings of greens each week, and at least two servings of berries each week.

Spices and chocolate
Spices and dark chocolate contain antioxidants called flavonoids. These compounds can help improve blood flow to the brain and reduce inflammation. These can be found in high amounts in turmeric, cinnamon, ginger, and dark and unsweetened chocolate.

Coffee and teas
Did you know that coffee can help to improve your memory and ward off dementia? Up to three cups of black coffee per day is recommended. When it comes to teas, black and green teas contain antioxidants for brain health.
Moderate consumption of red wine
Resveratrol is a compound found in red wine and the skin of red grapes. It is also an antioxidant and is thought to be able to reduce cell damage and protect against the formation of plaques in the brain. Too much alcohol is not good for your brain either, so it’s important not to overdo it. Try to stick with no more than one glass of red wine per day if you’re a woman and no more than two glasses per day if you’re a man. You can also consume resveratrol from drinking red grape juice, which has the added benefit of being alcohol-free.
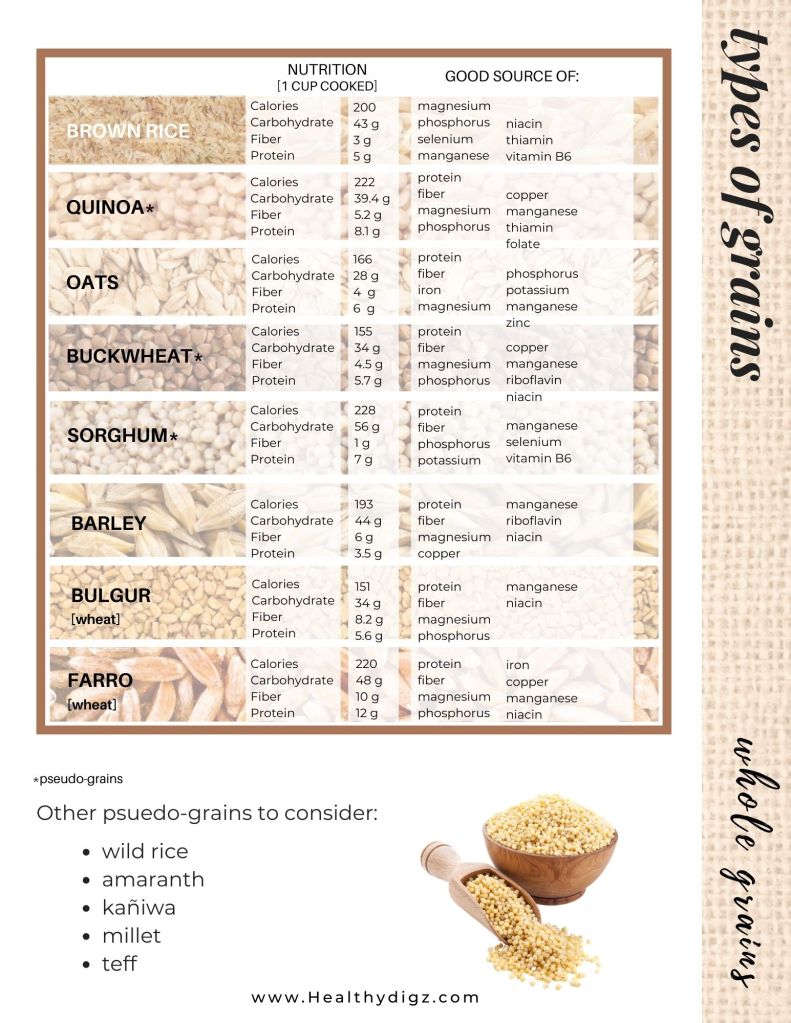
Whole grains
Whole grains like oats and quinoa are rich in brain-healthy B-vitamins and fiber, making them an important part of the MIND diet. B-vitamins are essential so that the brain can create energy, repair DNA, maintain the proper structure of neurons (nerve/brain cells), and create essential neurochemicals for optimal function. B-vitamins also act as antioxidants to reduce the harmful effects of free radicals that can damage all cells, including brain cells.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is also known as the “sunshine” vitamin because your skin makes it when it’s exposed to the sun. Low levels of vitamin D are associated with increased risks for brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s. You can increase your vitamin D levels by going in the sun for 5-15 minutes three times a week. You may need slightly more time if you have darker skin or live in a more northern latitude. Try not to get too much sun without sunscreen as it can increase your risk for skin cancer. Vitamin D supplements are also widely available but be sure to purchase reputable brands that sell products with third party certifications. You can learn more about dietary supplements and shop professional-grade products here.
Limit red meat
Consuming too many foods high in saturated fats is linked with an increased risk for heart disease and Alzheimer’s disease. The MIND diet recommends no more than four servings of red meat per week. Try limiting your red meat, butter, and dairy whenever you can and consider substituting with beans, lentils, and soy.
Final thoughts
There are many things you can do to bolster your brain health. They include a number of healthy habits such as getting exercise, reducing stress, getting enough sleep, socializing with others including with pets, and following recommendations for medications and supplements. When it comes to food and nutrition for brain health, try to get enough omega-3s, more plant foods, spices and chocolate, coffee and tea, vitamin D, and a bit of red wine. Limit the amount of red meat you consume.
If you’re interested in learning more about how you can implement these six essential brain health strategies into your life, consult a health professional who can help.